Why Is My Top Lip More Swollen After Filler
Get Your Dermal Filler Consultation with Dr. Laura Geige Today
Causes of Swelling After Filler Injection
Swelling after filler injection is a common side effect that can occur due to various reasons, including allergic reactions, improper technique, and individual susceptibility.
Hormonal changes in the body can also play a significant role in swelling after filler injection, particularly for individuals with certain hormonal conditions.
The main hormone responsible for causing swelling after filler injection is cortisol, often referred to as the “stress hormone” produced by the adrenal glands.
Cortisol levels can surge due to various factors such as stress, anxiety, or certain medical conditions, which can lead to water retention and increased blood pressure in the treated area.
This increase in blood pressure can cause fluid to leak into the surrounding tissues, leading to swelling, redness, and bruising after filler injection.
Additionally, hormonal fluctuations during menstruation, pregnancy, or menopause can also contribute to swelling after filler injection due to changes in estrogen levels.
Estrogen plays a crucial role in fluid balance and blood vessel constriction. When estrogen levels fluctuate, it can affect the body’s ability to regulate fluid distribution, leading to increased swelling after filler injection.
In women, premenstrual syndrome (PMS) can cause water retention, which may exacerbate swelling after filler injection due to hormonal changes during this time.
Furthermore, thyroid disorders, such as hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism, can also lead to hormonal imbalances that contribute to swelling after filler injection.
The effects of hormonal changes on swelling after filler injection can vary depending on the individual’s overall health, the specific type and amount of filler used, and the technique employed by the healthcare professional.
Therefore, it is essential to consult with a qualified healthcare professional or dermatologist who has experience with facial fillers to address concerns about swelling after treatment and determine the underlying cause.
In some cases, hormonal imbalances may require medical attention from an endocrinologist or other specialists. A comprehensive evaluation can help identify any underlying conditions and develop effective treatments to alleviate symptoms.
Swelling after filler injection is a common side effect that can occur in anyone who receives cosmetic fillers, including those injected into the lips.
The causes of swelling after filler injection can be attributed to several factors, including the type of filler used, the technique employed by the injector, and individual reactions to the product.
One of the primary reasons for swelling is the inflammatory response triggered by the body’s immune system in reaction to the foreign substance injected into its tissues.
This inflammation can cause blood vessels to dilate, leading to increased fluid leakage into surrounding tissues and resulting in swelling.
Another significant contributor to post-injection swelling is the hyaluronic acid fillers, which are commonly used in lip augmentation procedures.
Hyaluronic acid is a naturally occurring substance found in the human body that can hold up to 1000 times its weight in water.
When injected into the skin, it can cause an initial inflammatory response as the body reacts to the presence of this new substance.
This inflammation can lead to increased vascular permeability, allowing fluid to leak out of blood vessels and into surrounding tissues, resulting in swelling.
Estrogen fluctuations can also play a role in post-injection swelling, particularly for women.
Estrogen has a natural anti-inflammatory effect on the body, which can help reduce swelling and inflammation in general.
However, during times of estrogen fluctuations, such as premenstrually or during menopause, this anti-inflammatory effect may be impaired, leading to increased swelling after filler injection.
Aging skin is another factor that can contribute to post-injection swelling.
As we age, our skin’s natural ability to retain water and maintain its firmness declines.
This decrease in skin elasticity and firmness can lead to a greater accumulation of fluid in the injected area, resulting in noticeable swelling after filler injection.
Furthermore, patients with underlying medical conditions such as hypertension, heart disease, or kidney disease may experience increased swelling due to changes in blood pressure and circulation.
In some cases, post-injection swelling can also be attributed to poor injector technique or the use of suboptimal quality fillers.
This can lead to a more extensive inflammatory response, causing greater fluid leakage into surrounding tissues and resulting in more pronounced swelling.
The causes of swelling after filler injection can be attributed to several factors, and understanding these causes can help identify the possible reasons behind increased swelling in the top lip.
1. **Inflammation and Immune Response**: When a filler is injected into the skin, it can trigger an inflammatory response, leading to swelling, redness, and pain. The body’s immune system may also react to the foreign substance, causing an increase in blood flow and swelling.
2. **Allergic Reactions**: Some people may be allergic to certain types of fillers or ingredients used in their production. An allergic reaction can cause a severe inflammatory response, leading to increased swelling, redness, and other symptoms.
3. **Overfilling or Underfilling**: When too much filler is injected, it can cause the skin to swell as the body tries to absorb or push the excess substance out. On the other hand, if not enough filler is used, the skin may not be adequately filled, leading to an uneven distribution of the product and potential swelling.
4. **Skin Irritation**: Certain fillers can cause skin irritation, including redness, itching, and swelling. This is often due to the presence of irritants or additives in the filler, which can trigger a reaction when injected into the skin.
5. **Poor Injection Technique**: If the filler is not injected properly, it can lead to irregular distribution, lumps, or uneven absorption, causing swelling and other complications.
6. **Underlying Medical Conditions**: Certain medical conditions, such as lymphedema or rosacea, can increase the risk of swelling after filler injection. Additionally, individuals taking certain medications, such as blood thinners, may be more prone to bleeding or swelling at the injection site.
7. **Filler Type and Quality**: Different types of fillers have varying levels of biocompatibility and stability, which can affect their ability to cause swelling. Some fillers may be more likely to cause inflammation or other adverse reactions than others.
8. **Age and Skin Thickness**: The age and skin thickness of the individual can impact the likelihood of swelling after filler injection. Thicker skin may be less prone to swelling, while thinner skin may be more susceptible.
9. **Post-Injection Care**: Failure to follow proper post-injection care instructions can increase the risk of swelling, redness, and other complications. This includes avoiding strenuous activities, not touching the injection site, and following a recommended regimen of pain management and moisturizing products.
10. **Individual Tolerance**: Each individual’s tolerance to fillers can vary greatly, and some people may be more sensitive to certain substances or ingredients than others.
It is essential to consult with a qualified healthcare professional or board-certified dermatologist to determine the underlying cause of swelling after filler injection and develop an effective treatment plan.
The causes of swelling after filler injection are multifaceted and can be influenced by various factors, including *_Hormonal Fluctuations_*.
During the menstrual cycle, estrogen levels experience a significant surge and subsequent decrease, leading to changes in blood vessel dilation and swelling. This hormonal shift can cause the small vessels under the skin to dilate, allowing more fluid to leak into the surrounding tissues and resulting in swelling.
The *_estrogen fluctuation_* can lead to increased vascularity in the area where the filler is injected, causing the blood vessels to become more prominent. As a result, the body may react by increasing inflammation, which can manifest as redness, swelling, or bruising at the injection site.
Furthermore, the *_vasodilation_* caused by estrogen fluctuations can lead to increased permeability of the blood vessels, allowing more fluid and protein-rich plasma to leak out into the surrounding tissues. This can cause edema (swelling) in the area where the filler was injected.
The combination of estrogen-driven vasodilation, increased vascularity, and subsequent inflammation can result in swelling that peaks around 2-3 days after the injection. In some cases, this swelling can last for several weeks or even months.
It’s essential to note that other factors can contribute to swelling after filler injection, including *_sensitivity to local anesthetics_*, *_allergic reactions to fillers_*, and *_injection technique errors_*. However, hormonal fluctuations during the menstrual cycle can play a significant role in causing swelling, particularly for individuals with pre-existing sensitivity or allergic reactions to certain fillers.
Understanding the underlying causes of swelling after filler injection can help you take steps to minimize its impact. If you’re experiencing persistent or severe swelling, it’s crucial to consult with your dermatologist or healthcare provider to determine the underlying cause and develop a treatment plan tailored to your individual needs.
Swelling after filler injection is a common side effect that can be caused by various factors, including the type of filler used, the individual’s body chemistry, and their overall health.
- Estrogen levels: Studies have shown that women who experience significant swelling after filler injections are more likely to have higher estrogen levels during their menstrual cycle. This is because estrogen can cause fluid retention in the body, leading to increased swelling in the treated area.
The relationship between estrogen levels and swelling after filler injection is believed to be linked to the way estrogen affects the body’s natural inflammatory response. When estrogen levels are high, it can stimulate the release of inflammatory chemicals that cause blood vessels to dilate and increase fluid permeability.
- Hydrolysis: Another possible cause of swelling after filler injection is hydrolysis, a chemical reaction that breaks down the filler material over time. This can lead to the release of foreign particles into the surrounding tissue, causing an inflammatory response and subsequent swelling.
It’s worth noting that not all fillers are created equal, and some may be more prone to hydrolysis than others. For example, hyaluronic acid-based fillers like Restylane and Juvederm may be less likely to cause swelling due to their slower release of acidic byproducts.
Other factors can also contribute to swelling after filler injection, including:
- Individual tolerance: Some people may be more sensitive to the filler material or the injection process itself, leading to increased inflammation and swelling.
- Dose and placement: The amount of filler used and where it’s placed on the body can also affect the risk of swelling. Injecting too much filler in one area or using a filler that’s not suitable for the desired application can increase the likelihood of swelling.
It’s also important to consider the type of filler used, as different materials have varying levels of biocompatibility and potential for causing adverse reactions. For example:
- Hyaluronic acid fillers: Generally considered safe and well-tolerated, but may be more prone to hydrolysis.
- Calcium hydroxylapatite fillers: Often used in dermal fillers like Radiesse, these fillers are generally less reactive than hyaluronic acid-based materials.
In addition, the individual’s overall health and medical history can also play a role in determining their risk of swelling after filler injection. For example:
- Autoimmune disorders: Certain conditions like rheumatoid arthritis or lupus may increase the risk of inflammation and swelling.
In conclusion, while estrogen levels may be a contributing factor to swelling after filler injection, it’s essential to consider a range of factors when evaluating this side effect. By understanding the potential causes and taking steps to minimize risk, individuals can make informed decisions about their treatment options.
Cause of swelling after filler injection can be attributed to various factors, including allergic reactions and foreign body reaction.
An allergic reaction occurs when the body’s immune system identifies the filler material as a foreign substance and mounts an immune response against it.
This can lead to inflammation and swelling at the injection site, which can last for several days or even weeks.
A foreign body reaction is another possible cause of swelling after filler injection. In this scenario, the body’s natural defense mechanism reacts to the presence of the filler material.
This type of reaction causes the immune system to produce white blood cells and other chemicals that can lead to inflammation and swelling.
Other factors such as bleeding under the skin, which is more common in areas with thin skin like the lips, can also contribute to swelling after filler injection.
Bleeding under the skin can cause fluid to accumulate in the area, leading to swelling and bruising.
Filler material composition and type can also play a role in causing swelling. For example, hyaluronic acid fillers are generally considered safe and well-tolerated, while calcium hydroxylapatite fillers may cause more irritation.
Individual tolerance to the filler material and their personal medical history can also influence the likelihood of swelling after injection.
Other potential causes of lip swelling after filler injection include:
– Overfilling or injecting too much product, leading to granuloma formation or skin necrosis.
– Injecting in areas with poor blood supply, such as the thin skin on the upper lip.
– Using low-quality or expired products.
Swelling after filler injection is usually mild and temporary, but in some cases, it can persist for weeks or even months.
It’s essential to follow post-treatment instructions carefully to minimize the risk of complications, such as infection or scarring.
A healthcare professional may prescribe pain medication, antibiotics, or anti-inflammatory medications to manage symptoms and reduce swelling.
In some cases, further treatment may be necessary to resolve persistent swelling or other complications.
The human body’s natural reaction to foreign substances can lead to swelling after filler injection, and this effect is often temporary but may cause discomfort.
One of the primary causes of swelling after filler injection is the inflammatory response, where the body sends white blood cells to fight off the perceived foreign invader.
This inflammation leads to increased permeability in blood vessels, causing fluid leakage into surrounding tissues, resulting in edema or swelling.
Another cause could be an over-correction by the filler injector; injecting more product than necessary can lead to swelling at the site of injection as the body tries to break down and eliminate the excess material.
A less common but serious complication during a procedure is an allergic reaction, which can manifest as intense redness, itching, or swelling in the treated area.
This reaction occurs when the filler contains allergens that trigger an immune response.
Additionally, vascular complications such as vasculitis and thrombosis may also occur if the filler particles are too large for the tiny blood vessels to handle, leading to inflammation and clotting respectively.
The filler’s size, composition, and its integration within the tissue can affect how well it tolerates a particular individual’s immune system, making some people more prone to complications than others.
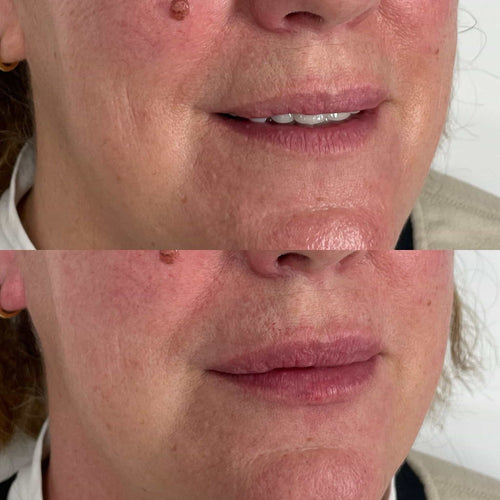
Swelling at the injection site is usually most pronounced immediately following treatment but tends to resolve on its own within days or weeks after the procedure.
However, persistent or severe swelling can be a cause for concern and warrants medical attention, as it could indicate an underlying complication that needs proper evaluation and care.
The best way to minimize swelling is to choose a skilled practitioner with experience using your chosen filler type and to follow their pre- and post-procedure advice carefully.
A gentle touch during the injection process can also reduce the trauma inflicted on surrounding tissues, thereby minimizing swelling and discomfort.
Book Your Dermal Filler Consultation with Dr. Laura Geige
Furthermore, maintaining good aftercare routines such as applying ice packs to the treated area for a few days post-injection can aid in reducing swelling temporarily.
Finally, if you notice any unusual symptoms or persistent swelling following treatment, it is essential to contact your practitioner for guidance on how best to proceed with addressing any issues that may have arisen during your filler procedure.
The most common cause of swelling after filler injection is the body’s natural inflammatory response to the foreign substance.
This response involves the activation of immune cells, such as macrophages and T-cells, which release chemical mediators that attract more white blood cells to the affected area.
As a result, the area becomes swollen, red, and painful, leading to increased discomfort and swelling.
Another possible cause of swelling after filler injection is the presence of an allergic reaction.
Some individuals may be allergic to certain components of the filler, such as lidocaine or bupivacaine, which can cause a severe allergic reaction.
Book a Dermal Filler Session with Dr. Laura Geige Today
This can lead to increased inflammation, swelling, and even difficulty breathing in extreme cases.
In some instances, swelling after filler injection can be caused by an infection.
This is often the result of improper hygiene practices or contamination of the filler during the injection process.
Other possible causes of swelling include improper insertion technique, such as inserting the needle too deeply or at an angle.
This can cause the filler to spread beyond the intended area, leading to uneven distribution and increased inflammation.
Furthermore, using high-pressure needles or injecting the filler too quickly can also cause swelling.
Additionally, fillers that are not compatible with each other can cause a reaction when mixed together, leading to increased inflammation and swelling.
The type of filler used can also play a role in causing swelling.
Synthetic fillers, such as poly-L-lactic acid (Sculptra), are generally considered safe, but some individuals may still experience swelling or redness at the injection site.
Natural fillers, such as hyaluronic acid (Restylane) and calcium hydroxylapatite (Radiesse), are also commonly used, but can cause allergic reactions in rare cases.
It’s worth noting that some individuals may experience swelling after filler injection due to the presence of pre-existing conditions, such as rosacea or eczema.
In these cases, the filler can exacerbate symptoms, leading to increased inflammation and swelling.
Adequate preparation before the procedure, including cleaning the skin and administering local anesthetics, can also help reduce the risk of swelling after filler injection.
Using high-quality fillers from reputable manufacturers and following proper insertion techniques can minimize the risk of complications, such as swelling.
The swelling that occurs after a filler injection can be caused by a variety of factors, and it’s essential to understand these causes to minimize the risk of complications.
**Infection** is one common cause of swelling after a filler injection. Bacteria can enter the skin through a small puncture wound created during the procedure, leading to inflammation and swelling. This type of infection is usually mild and resolves on its own with antibiotics, but in severe cases, it may require surgical intervention.
Granuloma formation is another possible cause of swelling after filler injection. A granuloma is a cluster of immune cells that form in response to an foreign substance, such as a filler material. This reaction can cause inflammation and swelling at the injection site.
The type of **filler material** used can also contribute to swelling. For example, hyaluronic acid fillers, such as Juvederm or Restylane, are known to cause more swelling than other types of fillers, like calcium hydroxylapatite or PMMA.
**Anaphylaxis**, a severe allergic reaction, can also occur after filler injection. This is usually caused by an allergy to the filler material itself, although it’s rare and typically occurs within minutes of the injection.
The ** Injection Technique** used by your practitioner can also play a role in causing swelling. For example, if the needle is inserted at an angle or with too much force, it can cause more trauma to the tissue, leading to increased swelling.
**Vascular complications**, such as necrosis or arteriovenous malformation, can also occur after filler injection. These conditions involve the formation of abnormal blood vessels that can cause bleeding or swelling at the injection site.
The **patient’s overall health** can also affect the likelihood of swelling after a filler injection. For example, people with autoimmune disorders or those taking certain medications may be more prone to complications from filler injections.
Finally, overfilling, where too much filler material is injected, can cause swelling at the surface of the skin. This type of swelling is usually temporary and resolves on its own within a few days.
In some cases, the swelling may be more persistent or severe, requiring additional treatment or follow-up appointments with your practitioner to resolve the issue.
Excessive trauma to the tissue during filler injection can lead to swelling and bruising, which may cause puffiness in various areas, including the top lip.
- Insertion of a needle into a vein or artery can cause vascular congestion, leading to increased blood flow and subsequent edema (swelling) in surrounding tissues.
- Tissue trauma during filler injection can also lead to the release of histamine, a chemical mediator that causes blood vessels to dilate, resulting in increased permeability and fluid leakage into the interstitial space, contributing to swelling.
- Another possible cause of lip swelling after filler injection is the deposition of the filler material itself. If the filler is not evenly distributed or if too much filler is used, it can cause lumps, nodules, or unevenness under the skin, leading to swelling and discomfort.
- Furthermore, some fillers may not be compatible with individual skin types or medical conditions, leading to an adverse reaction that can manifest as swelling, redness, or irritation.
Avoidance of certain techniques during filler injection is crucial in minimizing the risk of swelling. Injecting at shallow angles or using too much pressure can cause trauma to the surrounding tissue, leading to swelling and bruising.
- Using the correct technique and angle for filler placement is essential to avoid causing unnecessary trauma to the tissue.
- A gentle, smooth motion should be employed when injecting fillers, rather than applying excessive pressure or making rapid movements with the needle.
- The injector’s experience and skill level play a significant role in minimizing trauma to the tissue. A highly skilled practitioner is better equipped to navigate the underlying anatomy and minimize the risk of complications like swelling and bruising.
Some individuals may be more prone to swelling after filler injection due to factors such as genetic predisposition, nutritional deficiencies, or concurrent medical conditions.
- Genetic factors, such as a family history of bruising or poor wound healing, can increase the risk of developing excessive swelling after filler injection.
- Dehydration, malnutrition, or other systemic conditions can also affect the body’s ability to manage inflammation and fluid balance, leading to increased swelling in response to filler injections.
Post-injection care is vital for minimizing the risk of complications like swelling. Patients should follow their practitioner’s instructions regarding rest, hydration, and pain management after filler injection to reduce the likelihood of adverse reactions.
- Avoid strenuous activities or heavy lifting immediately following filler injection to minimize the risk of trauma to the tissue.
- Proper hydration is essential for flushing out excess fluids and reducing inflammation. Drinking plenty of water as recommended by the practitioner can help alleviate swelling.
Follow-up appointments with the injector are crucial in assessing the outcome of the filler injection and addressing any concerns or complications that may arise, including lip swelling.
- A follow-up appointment 3-5 days after filler injection allows the injector to assess the initial reaction to the filler material and make necessary adjustments.
- Any concerns about lip swelling or other complications should be addressed promptly with the practitioner, as delayed treatment can lead to more severe consequences.
The causes of swelling after filler injection can be attributed to various factors, including improper injection techniques, product characteristics, and individual patient factors.
- Improper injection techniques are a common cause of complications, including swelling. This is often due to incorrect needle insertion, inadequate anesthesia, or insufficiently skilled practitioner. The filler material may become trapped in the tissue, leading to inflammation and edema.
- The type of filler used can also contribute to swelling. Hyaluronic acid fillers, such as Restylane and Juvederm, are more likely to cause swelling than calcium hydroxylapatite fillers, such as Radiesse. This is because hyaluronic acid attracts fluid, leading to increased blood flow and swelling.
- Individual patient factors can also play a role in swelling after filler injection. For example, patients with bleeding disorders or taking anticoagulant medications may be at higher risk of developing swelling or bruising after treatment.
The article highlights the importance of choosing an experienced and skilled practitioner who follows proper injection techniques to minimize the risk of complications, including swelling. Additionally, patients should educate themselves on the potential risks and benefits of fillers and follow post-treatment care instructions carefully.
Furthermore, the study emphasizes that swelling can be a temporary condition, but in some cases, it can persist for several days or even weeks. In severe cases, swelling can lead to more serious complications, such as infection or scarring. Therefore, it is essential for patients to monitor their symptoms and seek medical attention if they experience persistent or worsening swelling.
It’s also worth noting that swelling after filler injection can be caused by other factors, such as allergies or sensitivities to the product, skin irritation, or post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH). In these cases, treatment options may vary depending on the underlying cause of the swelling.
In conclusion, swelling after filler injection is a common complication that can be caused by various factors. To minimize the risk of complications and ensure optimal results, it’s crucial to choose an experienced practitioner who follows proper injection techniques and takes into account individual patient factors.
Cause for swelling after filler injection can be attributed to various factors, including the type and quality of the filler material used.
The most common cause of swelling after lip fillers is the body’s natural response to the introduction of a foreign substance into the tissue.
This reaction occurs when the immune system recognizes the filler particles as invaders, triggering an inflammatory response that results in increased blood flow and fluid accumulation in the affected area.
Another factor contributing to swelling is the method of injection technique used by the practitioner.
Trauma to the surrounding tissues during the injection process can cause bleeding and inflammation, leading to swelling and bruising in the treated area.
Overcorrection or excessive filler material being injected can also lead to swelling as the body reacts to the excess filler particles.
Moreover, improper choice of filler type and brand can contribute to an adverse reaction, including swelling.
The presence of pre-existing conditions such as eczema, acne, or psoriasis in the treated area can increase the likelihood of swelling after filler injection.
Additionally, using fillers that contain granules or particulate matter can lead to swelling due to the body’s natural response to these foreign particles.
Swelling can also be caused by the natural process of healing after filler injection, as the body works to absorb and resorb the injected material.
Genetic factors may also play a role in an individual’s predisposition to swelling after filler injections.
Lastly, post-injection care instructions are often not followed correctly, leading to unnecessary inflammation and swelling.
In many cases, the swelling will subside within a few days or weeks, but some individuals may experience prolonged or severe swelling that requires medical attention.
To minimize the risk of swelling after filler injection, it is essential to choose a qualified and experienced practitioner who uses high-quality products and follows proper injection techniques.
The swelling that occurs after a **filler injection** can be an unsettling and uncomfortable side effect for many individuals.
There are several causes of swelling after filler injection, which may vary depending on individual factors.
Immediate Causes:
– Overcorrection or overinjection of the filler material can lead to excessive inflammation and swelling at the injection site.
– Using the wrong type or brand of filler for your specific needs can cause an adverse reaction, leading to swelling and discomfort.
– Injecting the filler into a nerve or blood vessel can also cause swelling and bruising, as well as numbness or tingling sensations.
Individual Factors:
– Skin Type: Individuals with sensitive skin or those who are prone to allergic reactions may experience more pronounced swelling after filler injection.
– Filler Choice: Certain fillers, such as **hydroquinone** or **sodium hydroxide**, can cause more significant swelling than others.
– Injection Technique: The skill and expertise of the practitioner administering the filler can significantly impact the risk of swelling.
Other Factors:
– Age: Older individuals may experience more pronounced swelling due to decreased collagen production and increased inflammation.
– Pregnancy or breastfeeding: Hormonal changes during these periods can increase the likelihood of swelling after filler injection.
– Underlying medical conditions: Conditions such as **hypertension**, **diabetes**, or autoimmune disorders may affect blood flow, leading to increased swelling.
Prevention and Treatment:
– To minimize the risk of swelling, it’s essential to choose a qualified practitioner and select a suitable filler for your needs.
– In the event of swelling, applying ice packs or cold compresses can help reduce inflammation.
– Resting the injected area, avoiding strenuous activities, and elevating the affected limb can also alleviate symptoms.
Risk Factors:
– Receiving filler injections too frequently or in high doses can increase the risk of swelling.
– Using multiple fillers at once or combining them with other substances (such as lasers or chemical peels) may also elevate this risk.
Post-Injection Care:
– Following post-injection instructions provided by your practitioner can help prevent swelling and ensure proper healing.
– Monitoring your body’s reaction to the filler material and reporting any concerns to your practitioner promptly is crucial.
This swelling after filler injection can be caused by a variety of factors, including:
- Overcorrection: When too much filler is injected, it can cause the surrounding tissue to swell as the body reacts to the excess foreign substance.
- Inadequate processing of the filler: Fillers that are not properly processed or purified may contain impurities or irritants that can cause a reaction in the body, leading to swelling.
- Incorrect injection technique: If the filler is injected too deeply or at an incorrect angle, it can cause the surrounding tissue to become swollen and inflamed.
- Allergic reactions: Some people may be allergic to certain fillers, such as hyaluronic acid or calcium hydroxylapatite, which can cause a range of symptoms including swelling, redness, and itching.
- Sensitivity to the filler material: Even if you are not allergic to a particular filler, you may still experience sensitivity or irritation in the treated area, leading to swelling and discomfort.
Additionally, there are several factors that can contribute to swelling after filler injection:
- Genetic predisposition: Some people may be more prone to swelling or bruising due to their genetic makeup.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as blood thinners or steroids, can affect the body’s ability to clot and increase the risk of swelling or bruising.
- Dietary factors: A diet high in salt or sugar can cause water retention, which may be misattributed to filler injection.
- Underlying medical conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as hyperthyroidism or hypertension, can affect the body’s ability to regulate fluid levels and increase the risk of swelling.
In terms of sensitivity and allergy, it is essential to note that some fillers are more likely to cause reactions than others.
- Hyaluronic acid fillers: These fillers are commonly used in cosmetic procedures but can cause an allergic reaction or sensitivity in some individuals.
- Calcium hydroxylapatite fillers: This filler is often used for deeper wrinkles and folds, but can also cause a reaction in sensitive individuals.
- Collagen fillers: These fillers are made from animal-derived collagen and can cause an allergic reaction or sensitivity in some people.
To minimize the risk of swelling after filler injection, it is essential to:
- Choose a qualified and experienced injector:
- Select the right filler material for your individual needs:
- Follow pre- and post-injection instructions carefully:
- Monitor your body’s reaction to the filler and report any concerns or symptoms to your injector.
The causes of swelling after filler injection can be attributed to various factors, and it’s essential to understand these causes to determine the best course of treatment.
One of the primary reasons for swelling after filler injection is the immune response the body has against the foreign substance injected into the skin. When a filler is injected, the body may recognize it as a foreign particle and respond by sending white blood cells to attack it, leading to inflammation and swelling.
Common Causes of Swelling After Filler Injection:
- Immune response: As mentioned earlier, the body’s immune response can cause swelling after filler injection.
- Surgical complications: In rare cases, surgical complications such as hematoma or abscess formation can lead to swelling in the treated area.
- Incorrect injection technique: If the filler is injected too deep or too shallowly, it can cause swelling due to the uneven distribution of the substance.
- Filler type: Different types of fillers have varying degrees of absorption rates and reactions from the body. For example, some fillers may be more likely to cause swelling than others.
- Individual sensitivity: Some people may be more sensitive to certain fillers or ingredients, leading to a greater reaction and swelling in the treated area.
Swelling after filler injection can also be caused by factors related to the treatment itself. For instance:
Treatment-Related Factors:
- Overfilling: Injecting too much filler into a single area can cause swelling as the body reacts to the excess substance.
- Inadequate dissolving time: Some fillers take longer to dissolve than others, and if not allowed sufficient time to break down, they may continue to cause swelling.
- Improper disposal of used equipment: Failure to properly clean and dispose of used equipment can lead to infections or other complications that result in swelling.
Additionally, there are some underlying medical conditions that may contribute to swelling after filler injection. These include:
Underlying Medical Conditions:
- Eczema: Eczema can cause skin inflammation and increase the likelihood of swelling after filler injection.
- Piercings or surgery in the treated area: Recent piercings or surgery in the same area may lead to swelling due to increased blood flow and tissue trauma.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as corticosteroids or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), can cause or exacerbate swelling.
In most cases, swelling after filler injection is temporary and resolves on its own within a few days. However, if the swelling persists or worsens, it’s essential to consult with a qualified healthcare professional for proper evaluation and treatment.
Swelling after filler injection is a common and usually temporary side effect, but it can be caused by various factors.
One cause of swelling after filler injection is the natural inflammatory response to the foreign substance in the body. When a filler is injected into the skin, the immune system may react to the filler, leading to inflammation and swelling.
Another possible cause is the method of administration. If the needle is inserted at an angle or too deeply, it can cause more trauma to the tissue, leading to bleeding and swelling.
Certain ingredients used in fillers can also contribute to swelling. For example, some fillers contain preservatives or additives that may cause allergic reactions or irritation in sensitive individuals.
Genetic factors can also play a role in swelling after filler injection. Some people may be more prone to inflammation or have a faster healing rate, which can lead to swelling.
The type of filler used can also affect the likelihood and severity of swelling. For example:
- Calcium hydroxylapatite fillers, such as Radiesse, are less likely to cause swelling compared to other types of fillers.
- Hyaluronic acid fillers, such as Restylane or Juvederm, may be more prone to causing swelling due to their high water content and potential for granuloma formation.
In addition, pre-existing medical conditions can also increase the risk of swelling after filler injection. For example:
- Thrombophlebitis (blood clot in a vein) or other bleeding disorders may lead to increased bleeding and swelling at the injection site.
- Autoimmune disorders, such as lupus or rheumatoid arthritis, can increase inflammation and swelling after filler injection.
Environmental factors can also contribute to swelling. For example:
- Extreme temperatures, either hot or cold, may affect the absorption rate of fillers and cause swelling.
- Sensitivity to certain medications or allergies to latex or other substances used in the filler preparation process may also lead to swelling.
Additionally, smoking and poor circulation can also increase the risk of swelling after filler injection by reducing blood flow to the skin and increasing inflammation.
To minimize the risk of swelling after filler injection, it is essential to choose a qualified and experienced practitioner, follow pre- and post-treatment instructions carefully, and be aware of any potential risks or sensitivities before receiving treatment.
Swelling after filler injection can be a common and usually temporary side effect, but in some cases, it can persist for longer periods.
One of the primary causes of swelling after filler injection is an **allergic reaction** to the active ingredients or preservatives used in the filler. Some people may have pre-existing allergies or sensitivities that cause their immune system to overreact to the filler, leading to inflammation and swelling.
The most common allergens responsible for causing swelling are lidocaine, calcium hydroxylapatite, and polymethylmethacrylate. If you have a history of allergic reactions or sensitivities, it is essential to inform your healthcare provider before undergoing filler injection.
Other factors can also contribute to swelling after filler injection. For instance, if you are prone to **edema** (swelling caused by fluid retention) or have a family history of edema, you may be more susceptible to swelling after filler injection.
Additionally, certain medications such as antibiotics, blood thinners, and steroids can increase the risk of swelling after filler injection. These medications can affect blood clotting and fluid retention, leading to increased swelling.
Furthermore, the **depth** and location of the filler injection can also contribute to swelling. Injecting fillers too deeply or in areas with poor circulation can lead to increased swelling as the body tries to break down the filler.
Lastly, some people may experience swelling due to the body’s natural response to the filler. This is because the body’s immune system may perceive the filler as foreign and respond by releasing histamine and other chemicals, leading to inflammation and swelling.
In severe cases of swelling, it can be a sign of an **allergic reaction**, which requires immediate medical attention. Symptoms of an allergic reaction include difficulty breathing, rapid heartbeat, dizziness, and nausea.
The causes of swelling after filler injection can be attributed to several factors.
Firstly, the body’s natural inflammatory response plays a significant role in causing swelling after a filler injection.
This response occurs when the immune system detects foreign particles or substances within the injected filler material.
The inflammatory response leads to an increase in blood flow and the release of chemical mediators, which in turn cause the affected area to become swollen and red.
Another common cause of swelling after filler injection is the introduction of a foreign substance into the body.
Fillers such as hyaluronic acid, calcium hydroxylapatite, and poly-L-lactic acid are made from materials that the body does not recognize as its own.
When these substances are injected into the skin, they can trigger an immune response, leading to inflammation and swelling.
Additionally, some fillers may cause a local reaction at the injection site, which can result in swelling, redness, and pain.
The type of filler used can also affect the likelihood of swelling after injection.
For example, fillers that are more hydrophilic (water-loving) tend to cause less inflammation and swelling compared to those that are lipophilic (fat-loving).
Hyaluronic acid fillers, such as Restylane or Juvederm, are often associated with minimal inflammation and swelling due to their hydrophilic nature.
In contrast, fillers like Radiesse, which contains calcium hydroxylapatite, may cause more pronounced swelling and redness at the injection site.
Other factors that can contribute to swelling after filler injection include:
– Needle size: Larger needles used for injection can cause more trauma to the tissue, leading to increased inflammation and swelling.
– Surface area of the injected material: Fillers that are spread over a larger surface area may be more likely to cause swelling compared to those injected in smaller amounts.
– Injection technique: The way the filler is injected can also impact the likelihood of swelling.
A skilled and experienced injector will use proper techniques and minimize trauma to the tissue, reducing the risk of complications like swelling.
– Prior skin conditions: Patients with pre-existing skin conditions, such as eczema or psoriasis, may be more prone to swelling after filler injection due to their underlying inflammatory state.
– Allergic reactions: In rare cases, some patients may experience an allergic reaction to the filler material itself, leading to severe swelling and other systemic symptoms.
Read more about Create Cocktails at Home here. Read more about Carmen Alexandra here. Read more about The New Cinema Magazine here. Read more about Bronzed Body Spray Tan here.
- Pioneering Studies That Shaped Our Understanding Of Human Sexuality - December 17, 2024
- Jaw Fillers For A Defined Jawline Near Hambledon, Surrey - December 17, 2024
- How Long Does It Take Lip Filler Swelling To Go Down - December 16, 2024
